YOLOv5
YOLOv5 is a recent model developed by Ultralytics. It is a simple use, fast and accurate object detection model. It also allows for training with different weights, which enables the user to choose their model size and resource cost.
Enviroment
Enabling CUDA capabilities for both running the models and training them can be conflicting with most environments. Ultralytics has provided a CUDA compatible dockerfile over which both inference and training can be easily performed.
Run with GPU support
The following command will enable both GPU support (without any further setup) and will mount the current terminal directory, so it can access user files for both detect and training results to be accessed and stored.
To use a specific GPU device:
Usage
The YOLOv5 repository from ultralytics has an extensive documentation on detecting and training. It also provides python scripts that allow for easy training and detection tests. To train a model on YOLOv5:
Dataset
Datasets for training have a specific format that consists of a folder with the following structure:
Dataset
│ data.yaml
└─── train
│ └─── images
| | image1.png
| | image2.png
| | ...
| └───labels
| image1.txt
| image2.txt
| ...
└─── test
| ...
└─── validate
...
names:
- nameofclass1
- nameofclass2
...
nc: (numberofclasses)
test: ../test/images
train: ../train/images
val: ../validate/images
Sample annotation:
Training
Training on YOLOv5 is done with a single python script that accepts several arguments regarding its cofiguration and the dataset used for it. For this, the YOLOv5 repository has to be cloned locally:
Then, mount the docker image on a folder with access to the repository, and cd to the yolov5 folder. The train.py script has many arguments to be edited, but the recommended ones are shown on the following sample command:python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 300 --data $(pwd)/pathToDataset/dataset1/data.yaml --weights yolov5m.pt --name trainTest --cache --patience 50
The weights of the model will define the size of the trained model's file, as well as the requirements it will ask for the computer on which the inference will run. The repository currently has 6 default weights that can be used:
With the following precision and speed each: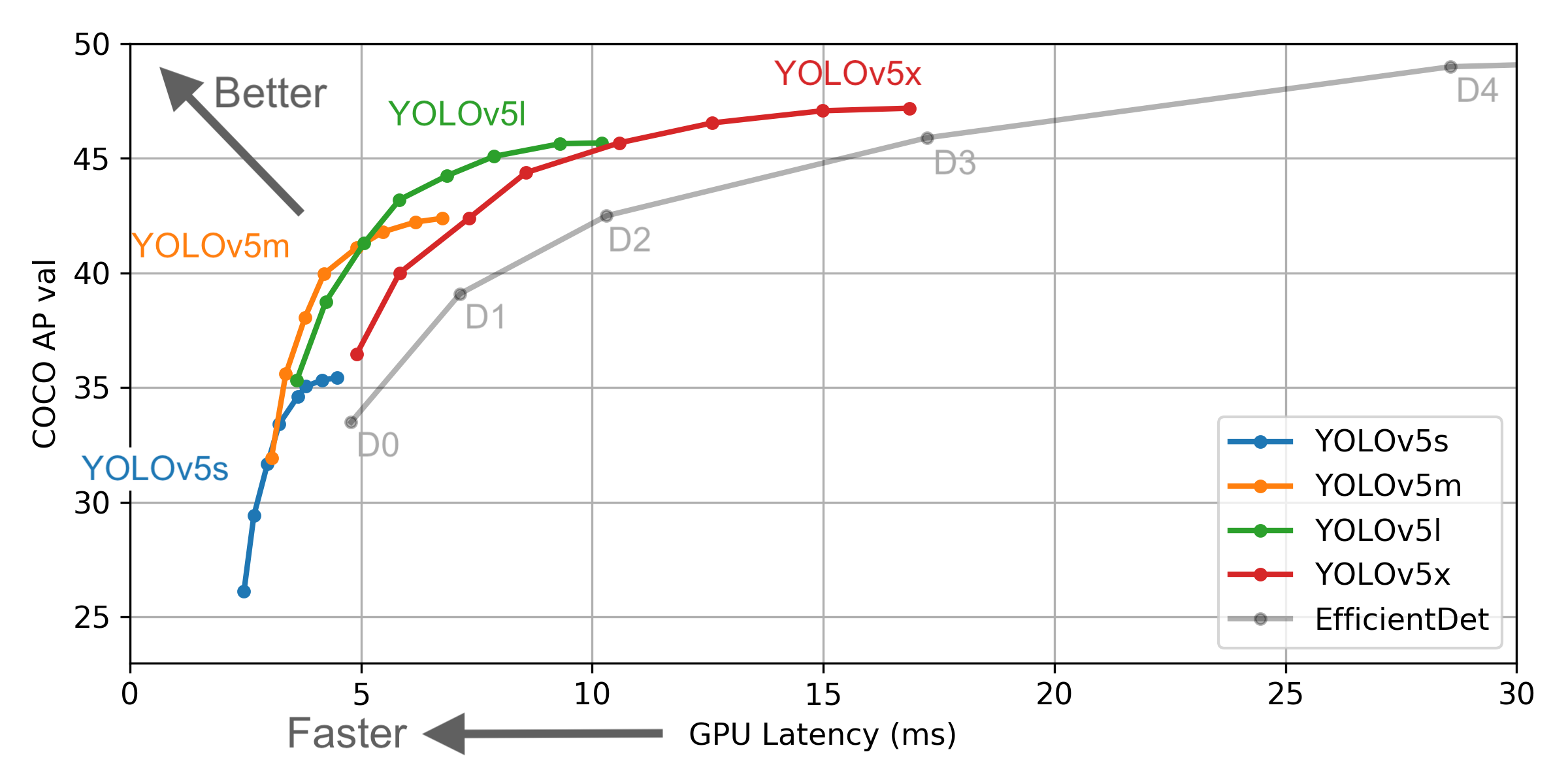 With testing, yolov5m has proven of enough accuracy while occupying less than 2GB of VRAM allocated on runtime.
With testing, yolov5m has proven of enough accuracy while occupying less than 2GB of VRAM allocated on runtime.
After training has finished, it will create a new folder on runs/train. There the created models will be contained on the weights folder, including the one generated on the last epoch of the training and the one with the best average precision. The folder will also include the results statistics in a graphical and as a CSV file.
To validate and test the model, it is recommended to use the tutorial.ipynb notebook, which already contains the commands to run both the detect.py and validate.py scripts. Both will generate folders on /runs with the results.
Sample results:

Detection was made using the YOLO ROS Wrapper available at: